Database Access with SQL Server on Azure
Teleport can provide secure access to Azure SQL Server via the Teleport Database Service. This allows for fine-grained access control through Teleport's RBAC.
In this guide, you will:
- Configure an Azure SQL Server using Azure Active Directory authentication.
- Join the Azure SQL Server database to your Teleport cluster.
- Connect to the Azure SQL Server database via the Teleport Database Service.
- Self-Hosted
- Teleport Enterprise Cloud
Prerequisites
Database access for Azure SQL Server with Azure Active Directory authentication
is available starting from Teleport 11.0.
-
A running Teleport cluster version 14.3.33 or above. If you want to get started with Teleport, sign up for a free trial or set up a demo environment.
-
The
tctladmin tool andtshclient tool.Visit Installation for instructions on downloading
tctlandtsh.
- SQL Server running on Azure.
- The Teleport Database Service running on an Azure virtual instance.
- To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials.tctlis supported on macOS and Linux machines. For example:If you can connect to the cluster and run the$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=email@example.com
$ tctl status
# Cluster teleport.example.com
# Version 14.3.33
# CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions.
Step 1/8. Create a Teleport user
To modify an existing user to provide access to the Database Service, see Database Access Access Controls
- Teleport Community Edition
- Teleport Enterprise/Enterprise Cloud
Create a local Teleport user with the built-in access role:
$ tctl users add \
--roles=access \
--db-users="*" \
--db-names="*" \
alice
Create a local Teleport user with the built-in access and requester roles:
$ tctl users add \
--roles=access,requester \
--db-users="*" \
--db-names="*" \
alice
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
--roles | List of roles to assign to the user. The builtin access role allows them to connect to any database server registered with Teleport. |
--db-users | List of database usernames the user will be allowed to use when connecting to the databases. A wildcard allows any user. |
--db-names | List of logical databases (aka schemas) the user will be allowed to connect to within a database server. A wildcard allows any database. |
Database names are only enforced for PostgreSQL and MongoDB databases.
For more detailed information about database access controls and how to restrict access see RBAC documentation.
Step 2/8. Enable the SQL Server Azure Active Directory integration
If you have it enabled, you can go to the next step.
Go to the Azure Portal, select Database servers, and select the database you wish to enable the Azure Active Directory integration.
Select Azure Active Directory in the left-hand column.
Select Set Admin, and choose an account that will be added as an admin login to SQL Server.
Step 3/8. Configure IAM permissions for Teleport
The Teleport Database Service needs Azure IAM permissions to:
- Discover and register SQL Server instances.
- Fetch virtual machine managed identities used for login.
Configure an Azure service principal
Teleport requires the following permissions:
<resource-type>/readpermissions for discovery, but only for the resource types you have. For example,Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances/read.Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/read.
Here is a sample role definition allowing Teleport to read Azure SQL Servers and Azure SQL Managed Instances:
{
"properties": {
"roleName": "SQLServerAutoDiscovery",
"description": "Allows Teleport to discover SQL Servers and SQL Managed Instances.",
"assignableScopes": [
"/subscriptions/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
],
"permissions": [
{
"actions": [
"Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances/read",
"Microsoft.Sql/servers/read",
"Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/read"
],
"notActions": [],
"dataActions": [],
"notDataActions": []
}
]
}
}
The assignableScopes field above includes a subscription
(/subscriptions/<subscription>), allowing the role to be assigned at any
resource scope within that subscription or the subscription scope itself.
If you want to further limit the assignableScopes, you can use a resource
group (/subscriptions/<subscription>/resourceGroups/<group>) or a management
group (/providers/Microsoft.Management/managementGroups/<group>) instead.
Go to the Subscriptions page and select a subscription.
Click on Access control (IAM) in the subscription and select Add > Add custom role:
In the custom role creation page, click the JSON tab and click Edit,
then paste the JSON example and replace the subscription in assignableScopes
with your own subscription id:
Step 4/8. Configure virtual machine identities
In the Teleport Database Service virtual machine's Identity section, enable the system assigned identity. This is used by Teleport to access Azure APIs.
To grant Teleport permissions, the custom role you created must be assigned to the virtual machine system assigned identity. On the same page, click on the Azure role assignments, then on Add role assignment. Select the custom role and save.
The role assignment should be at a high enough scope to allow the Teleport Database Service to discover all matching databases. See Identify the needed scope for more information about Azure scopes and creating role assignments.
Login identities
The Teleport Database Service needs access tokens from Azure AD to authenticate with SQL Server databases.
It uses the managed identities attached to its Virtual Machine to fetch the authentication token.
To create a new user-assigned managed identity, go to the Managed Identities page in your Azure Portal and click on Create. Choose a name and resource group for it and create:
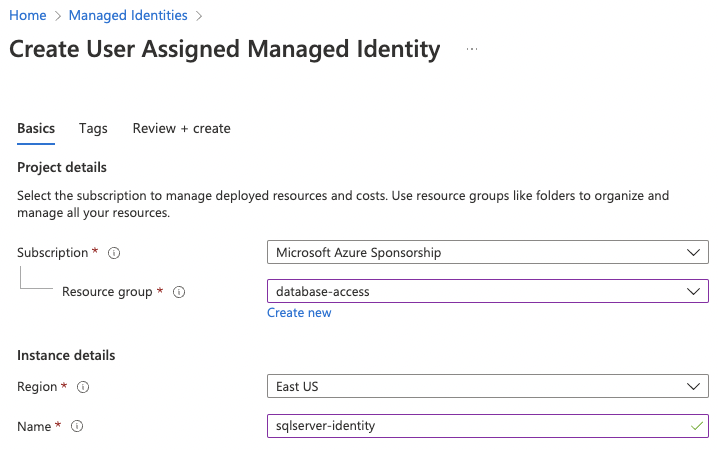
Next, go to the Teleport Database Service virtual machine instance, Identity section, select User assigned, and add the identity we just created:
Step 5/8. Enable managed identities login on SQL Server
Azure AD SQL Server integration uses database-level authentication (contained users), meaning we must create a user for our identities on each database we want to access.
To create contained users for the identities, connect to your SQL server using its Activity Directory Admin and execute the query:
USE MyDatabase;
CREATE USER [sqlserver-identity] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
The newly created user will be attached to the public role, which might not
have enough permissions to perform queries. Consider granting individual
permissions to the user or assigning it to an existing role. For example, add
the user as a member of the db_datareader role:
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [sqlserver-identity];
Step 6/8. Create a Database Service configuration
Install Teleport on the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service:
Select an edition, then follow the instructions for that edition to install Teleport.
- Teleport Community Edition
- Teleport Enterprise
- Teleport Enterprise Cloud
The following command updates the repository for the package manager on the local operating system and installs the provided Teleport version:
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/install-v14.3.33.sh | bash -s 14.3.33
- Debian 9+/Ubuntu 16.04+ (apt)
- Amazon Linux 2/RHEL 7 (yum)
- Amazon Linux 2/RHEL 7 (zypper)
- Amazon Linux 2023/RHEL 8+ (dnf)
- SLES 12 SP5+ and 15 SP5+ (zypper)
- Tarball
# Download Teleport's PGP public key
$ sudo curl https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/gpg \
-o /usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport APT repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc] \
https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/${ID?} ${VERSION_CODENAME?} stable/v14" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/teleport.list > /dev/null
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install teleport-ent
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo apt-get install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
# First, get the major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils
$ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/v14/teleport.repo")"
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent
#
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport Zypper repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use zypper to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh --repo $(rpm --eval "https://zypper.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-zypper.repo")
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent
#
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo yum install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for v14. You'll need to update this
# file for each major release of Teleport.
# First, get the major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use the dnf config manager plugin to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/v14/teleport.repo")"
# Install teleport
$ sudo dnf install teleport-ent
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo dnf install teleport-ent-fips
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport Zypper repository.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use Zypper to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh --repo $(rpm --eval "https://zypper.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/v14/teleport-zypper.repo")
# Install teleport
$ sudo zypper install teleport-ent
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations, install the teleport-ent-fips package instead:
$ sudo zypper install teleport-ent-fips
In the example commands below, update $SYSTEM_ARCH with the appropriate
value (amd64, arm64, or arm). All example commands using this variable
will update after one is filled out.
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz.sha256
# <checksum> <filename>
$ curl -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz
$ shasum -a 256 teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz
# Verify that the checksums match
$ tar -xvf teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-bin.tar.gz
$ cd teleport-ent
$ sudo ./install
For FedRAMP/FIPS-compliant installations of Teleport Enterprise, package URLs will be slightly different:
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz.sha256
# <checksum> <filename>
$ curl -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz
$ shasum -a 256 teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz
# Verify that the checksums match
$ tar -xvf teleport-ent-v14.3.33-linux-$SYSTEM_ARCH-fips-bin.tar.gz
$ cd teleport-ent
$ sudo ./install
OS repository channels
The following channels are available for APT, YUM, and Zypper repos. They may be used in place of
stable/v14 anywhere in the Teleport documentation.
| Channel name | Description |
|---|---|
stable/<major> | Receives releases for the specified major release line, i.e. v14 |
stable/cloud | Rolling channel that receives releases compatible with current Cloud version |
stable/rolling | Rolling channel that receives all published Teleport releases |
- Debian 9+/Ubuntu 16.04+ (apt)
- Amazon Linux 2/RHEL 7/CentOS 7 (yum)
- Amazon Linux 2023/RHEL 8+ (dnf)
- SLES 12 SP5+ and 15 SP5+ (zypper)
Add the Teleport repository to your repository list:
# Download Teleport's PGP public key
$ sudo curl https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/gpg \
-o /usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport APT repository for cloud.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/teleport-archive-keyring.asc] \
https://apt.releases.teleport.dev/${ID?} ${VERSION_CODENAME?} stable/cloud" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/teleport.list > /dev/null
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Update the repo and install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install "teleport-ent=$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for cloud.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils
$ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-yum.repo")"
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo yum install "teleport-ent-$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport YUM repository for cloud.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use the dnf config manager plugin to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo "$(rpm --eval "https://yum.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-yum.repo")"
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo dnf install "teleport-ent-$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
# Tip: Add /usr/local/bin to path used by sudo (so 'sudo tctl users add' will work as per the docs)
# echo "Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin" > /etc/sudoers.d/secure_path
# Source variables about OS version
$ source /etc/os-release
# Add the Teleport Zypper repository for cloud.
# First, get the OS major version from $VERSION_ID so this fetches the correct
# package version.
$ VERSION_ID=$(echo $VERSION_ID | grep -Eo "^[0-9]+")
# Use Zypper to add the teleport RPM repo
$ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh --repo $(rpm --eval "https://zypper.releases.teleport.dev/$ID/$VERSION_ID/Teleport/%{_arch}/stable/cloud/teleport-zypper.repo")
# Provide your Teleport domain to query the latest compatible Teleport version
$ export TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ export TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"
# Install Teleport and the Teleport updater
$ sudo zypper install "teleport-ent-$TELEPORT_VERSION" teleport-ent-updater
OS repository channels
The following channels are available for APT, YUM, and Zypper repos. They may be used in place of
stable/v14 anywhere in the Teleport documentation.
| Channel name | Description |
|---|---|
stable/<major> | Receives releases for the specified major release line, i.e. v14 |
stable/cloud | Rolling channel that receives releases compatible with current Cloud version |
stable/rolling | Rolling channel that receives all published Teleport releases |
Is my Teleport instance compatible with Teleport Enterprise Cloud?
Before installing a teleport binary with a version besides v16,
read our compatibility rules to ensure that the binary is compatible with
Teleport Enterprise Cloud.
Teleport uses Semantic Versioning. Version numbers
include a major version, minor version, and patch version, separated by dots.
When running multiple teleport binaries within a cluster, the following rules
apply:
- Patch and minor versions are always compatible, for example, any 8.0.1 component will work with any 8.0.3 component and any 8.1.0 component will work with any 8.3.0 component.
- Servers support clients that are one major version behind, but do not support
clients that are on a newer major version. For example, an 8.x.x Proxy Service
instance is compatible with 7.x.x agents and 7.x.x
tsh, but we don't guarantee that a 9.x.x agent will work with an 8.x.x Proxy Service instance. This also means you must not attempt to upgrade from 6.x.x straight to 8.x.x. You must upgrade to 7.x.x first. - Proxy Service instances and agents do not support Auth Service instances that
are on an older major version, and will fail to connect to older Auth Service
instances by default. You can override version checks by passing
--skip-version-checkwhen starting agents and Proxy Service instances.
Generate a configuration file at /etc/teleport.yaml for the Database Service.
Set the --proxy command-line option to the address for your Teleport cluster
and the --azure-sqlserver-discovery to the appropriate region:
$ sudo teleport db configure create \
-o file \
--token=/tmp/token \
--proxy=teleport.example.com:443 \
--azure-sqlserver-discovery=eastus
The command will generate a Database Service configuration with Azure SQL
Server auto-discovery enabled in the eastus region and place it at the
/etc/teleport.yaml location.
Step 7/8. Start Teleport Database Service
Configure the Teleport Database Service to start automatically when the host boots up by creating a systemd service for it. The instructions depend on how you installed the Teleport Database Service.
- Package Manager
- TAR Archive
On the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service, enable and start Teleport:
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport
$ sudo systemctl start teleport
On the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service, create a systemd service configuration for Teleport, enable the Teleport service, and start Teleport:
$ sudo teleport install systemd -o /etc/systemd/system/teleport.service
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport
$ sudo systemctl start teleport
You can check the status of the Teleport Database Service with systemctl status teleport
and view its logs with journalctl -fu teleport.
A single Teleport process can run multiple different services, for example multiple Database Service agents as well as the SSH Service or Application Service.
Step 8/8. Connect
Log in to your Teleport cluster. Your database should appear in the list of available databases:
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=alice
$ tsh db ls
Name Description Allowed Users Labels Connect
------------------ ---------------------------------- ------------- ------ -------
sqlserver Azure SQL Server in westeurope [*] ...
sqlserver-managed Azure Managed SQL Server in eastus [*] ...
To retrieve credentials for a database and connect to it:
$ tsh db connect --db-user=sqlserver-identity --db-name=master sqlserver
Where --db-user is the managed identity name.
Either the sqlcmd or mssql-cli command-line clients should be available in
PATH in order to be able to connect. tsh attempts to run sqlcmd first and,
if it's not present on the PATH, runs mssql-cli.
If you have neither command-line clients available on your system, you can run the following command to start a local proxy server that you can connect to with your SQL Server client:
$ tsh proxy db --db-user=teleport --tunnel sqlserver
Read the Database Access GUI Clients guide for how to connect your DB GUI client to the local proxy.
Troubleshooting
Could not find identity
If you see the error could not find identity "my-identity" attached to the instance when connecting to your database, then the identity you’re trying to
connect with is not attached to the Teleport Database Service virtual machine.
You can navigate to the Virtual Machines page within Azure Portal,
open the Teleport instance, Identity section, and choose User
assigned to see all identities you can connect with. If you don’t see your
identity check Step 4 to see how
to add it.
Login failed for the user
When connecting to your database, and you see the error mssql: login error: Login failed for user '<token-identified principal>', it means your managed identity
login is not present on the SQL database. You’ll need to create their users as
described in Step 6.
Remember: you must create the users on all databases you want to connect.
Timeout connecting to the database
If you receive the error i/o timeout issue when connecting to your database,
please check if the Teleport Database service can reach the database on
Azure.
In case your database is public, you can enable it to receive connections from Azure services without creating firewall rules: Go to your database page, Network tab, and at the bottom of the page in the Exceptions section check the option "Allow Azure services and resources to access this server" and save.
If your database is not public and it is using private endpoints, ensure that they're on the same VPC, or if the Teleport VM VPC is peering with the database one.
To check if the VM has access, you can do the following on the VM:
- Using
netcat:nc -v yourdatabase.database.windows.net 1433 - Using
telnet:telnet yourdatabase.database.windows.net 1433
Next steps
- Learn how to restrict access to certain users and databases.
- Learn more about dynamic database registration.
- View the High Availability (HA) guide.
- See the YAML configuration reference for updating dynamic resource matchers or static database definitions.
- Take a look at the full CLI reference.