Teleport Authentication with Keycloak
This guide explains how to configure Keycloak to issue credentials to specific groups of users with a SAML authentication connector. When used in combination with role-based access control (RBAC), it allows Teleport administrators to define policies like:
- Only members of the "DBA" group can connect to PostgreSQL databases.
- Developers must never SSH into production servers.
The following steps configure an example SAML authentication connector matching Keycloak groups. You can choose to configure other options.
How it works
You can register your Teleport cluster as an application with Keycloak, then create an authentication connector resource that provides Teleport with information about your application. When a user signs in to Teleport, Keycloak executes its own authentication flow, then sends an HTTP request to your Teleport cluster to indicate that authentication has completed.
Teleport authenticates users to your infrastructure by issuing short-lived certificates. After a user completes an SSO authentication flow, Teleport issues short-lived TLS and SSH certificates to the user. Teleport also creates a temporary user on the Auth Service backend.
Teleport roles are encoded in the user's certificates. To assign Teleport roles to the user, the Auth Service inspects the role mapping within the authentication connector, which associates user data on Keycloak with the names of one or more Teleport roles.
Prerequisites
Before you get started, you’ll need:
- An administrative account for the Keycloak Admin Console to manage realms and perform administrative tasks.
- To be in a realm other than the master realm.
- To register one or more users in the realm directory.
- To create at least two groups in realm directory and assign one or more users to each group.
- A Teleport role with access to maintaining
samlresources. This is available in the defaulteditorrole.
-
A running Teleport cluster version 18.0.0 or above. If you do not have one, read Get Started with Teleport or set up a demo environment.
-
The
tctlandtshclients.Installing
tctlandtshclients- Mac
- Windows - Powershell
- Linux
Download the signed macOS .pkg installer for Teleport, which includes the
tctlandtshclients:curl -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-18.0.0.pkgIn Finder double-click the
pkgfile to begin installation.dangerUsing Homebrew to install Teleport is not supported. The Teleport package in Homebrew is not maintained by Teleport and we can't guarantee its reliability or security.
curl.exe -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-v18.0.0-windows-amd64-bin.zipUnzip the archive and move the `tctl` and `tsh` clients to your %PATH%
NOTE: Do not place the `tctl` and `tsh` clients in the System32 directory, as this can cause issues when using WinSCP.
Use %SystemRoot% (C:\Windows) or %USERPROFILE% (C:\Users\<username>) instead.
All of the Teleport binaries in Linux installations include the
tctlandtshclients. For more options (including RPM/DEB packages and downloads for i386/ARM/ARM64) see our installation page.curl -O https://cdn.teleport.dev/teleport-v18.0.0-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gztar -xzf teleport-v18.0.0-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gzcd teleportsudo ./installTeleport binaries have been copied to /usr/local/bin
The
tctlandtshclients must be at most one major version behind your Teleport cluster version. Send a GET request to the Proxy Service at/v1/webapi/pingand use a JSON query tool to obtain your cluster version:curl https://example.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/ping | jq -r '.server_version'18.0.0
- To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials. For example, run the following command, assigning teleport.example.com to the domain name of the Teleport Proxy Service in your cluster and email@example.com to your Teleport username:If you can connect to the cluster and run thetsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=email@example.comtctl statusCluster teleport.example.com
Version 18.0.0
CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678
tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions.
Step 1/3. Configure Keycloak
Create a SAML Client
-
Select the Realm to be used for your SAML integration. Click Clients in the menu.
-
Click Create client
-
Set Client type to SAML and Set a Client ID to the URL for your Teleport Proxy Service URL
https://mytenant.teleport.sh -
Set the Valid Redirect URIs field to the URL for your Teleport Proxy Service host and Save
https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloakClick Save before proceeding to the next step.
Configure SAML assertion mappings
-
Navigate to Clients in left sidebar
-
Select your Teleport SAML client, Navigate to the Client Scope tab
-
On the Client Scopes Tabs , click on the Teleport client scope
-
On the Mappers tab, Click Configure a new mapper.
-
Select Groups list from the list of attribute mappings
-
Fill out the values as shown in the image below and Save
-
Repeat steps 1 - 6 to add the User Attribute mapper.
-
Fill out the values as shown in the image below and Save.
This enables using the username inside Teleport roles as the
{{external.username}}
Step 2/3. Create a new Teleport role
Create a Teleport role resource that will use external username data from the Keycloak connector to determine which Linux logins to allow on a host.
Create a file called dev.yaml with the following content:
kind: role
version: v5
metadata:
name: dev
spec:
options:
max_session_ttl: 24h
allow:
# only allow login as either ubuntu or the 'windowsaccountname' claim
logins: [ '{{external.username}}', ubuntu ]
node_labels:
access: relaxed
Users with the dev role are only allowed to log in to nodes with the access: relaxed Teleport label. They can log in as either ubuntu or a username that
is passed in from the keycloak connector using the username
attribute.
The login
{{external.username}}username
attribute and use that field as an allowed login for each user.
Create the role:
tctl create dev.yaml
Enable default SAML authentication
Configure Teleport to use SAML authentication as the default instead of the local user database.
Use tctl to edit the cluster_auth_preference value:
tctl edit cluster_auth_preference
Set the value of spec.type to saml:
kind: cluster_auth_preference
metadata:
...
name: cluster-auth-preference
spec:
...
type: saml
...
version: v2
After you save and exit the editor, tctl will update the resource:
cluster auth preference has been updated
If you need to log in again before configuring your SAML provider, use the flag --auth=local
Step 3/3. Create a SAML connector
Now, create a SAML connector resource using tctl.
tctl sso configure saml --name keycloak \--entity-descriptor https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}/protocol/saml/descriptor \--attributes-to-roles groups,/devops,dev \--audience https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak \--acs https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak > keycloak-connector.yaml
In the example above:
--entity-descriptorspecifies the app federation metadata URL- Each
--attributes-to-rolesspecifies the name of the schema definition for groups, groups, the name of a Keycloak group and the Teleport role that members of the group will be assigned. - Keycloak includes an explicit leading
/in the group name, which is reflected in the group name specified in the above example. --acsspecifies where the SAML provider makes callbacks after successful authentication.--audienceuniquely identifies your service provider (Teleport).
The file keycloak-connector.yaml should now resemble the following:
kind: saml
metadata:
name: keycloak
spec:
acs: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
attributes_to_roles:
- name: groups
roles:
- dev
value: /devops
audience: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
cert: ""
display: ""
entity_descriptor: ""
entity_descriptor_url: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}/protocol/saml/descriptor
issuer: ""
service_provider_issuer: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
sso: ""
version: v2
To optionally test the auth connector, temporarily disable the Client signature required option by navigating to the Keys tab of the SAML client. This will be enabled at a later step as you proceed through the guide.
With the connector in place on the cluster, you can test it with tctl:
cat keycloak-connector.yaml | tctl sso test
Your browser should open and log you in to the Teleport cluster using your Keycloak user credentials. If there are any problems, the CLI output will help you debug the connector configuration.
To create the connector using the tctl tool, run the following command:
tctl create -f keycloak-connector.yaml
Client Certificate Signature validation (Recommended)
If Client Signature Required is enabled, documents coming from the client are expected to be signed. Keycloak will validate this signature using the client public key or cert set up in the Keys tab.
To have Keycloak require client signature validation from Teleport, you must configure the signing keys by generating and importing keys to Keycloak, The client will sign their saml requests and responses and the signature will be validated.
Create private keys for signing
- Start by generating a private key and certificate.
openssl genrsa -out priv.pem 2048openssl req -new -x509 -key priv.pem -out cert.pem
- Convert the just generated certificate (in PEM format) to the PKCS#12 format
openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -name teleport -export -out cert.pkcs12
Take note of the name and the defined export password as it will be used when importing the cert to Keycloak.
tctl edit saml/keycloak
You will notice that Teleport has generated a signing_key_pair. This key pair
is used to sign responses.
kind: saml
metadata:
name: keycloak
spec:
acs: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/azure-saml
attributes_to_roles:
- name: groups
roles:
- editor
- access
- auditor
value: '*'
audience: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
cert: ""
display: Keycloak
entity_descriptor:
entity_descriptor_url: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}/protocol/saml/descriptor
issuer: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}
service_provider_issuer: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
signing_key_pair:
cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
private_key: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
sso: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}/protocol/saml
version: v2
Add assertion_key_pair using the data from cert.pkcs12.
Make sure to have the same indentation for all lines of the certificate and key, otherwise Teleport will not parse the YAML file.
After your edits, the file will look like this:
kind: saml
metadata:
name: keycloak
spec:
acs: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/azure-saml
attributes_to_roles:
- name: groups
roles:
- editor
- access
- auditor
value: '*'
audience: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
cert: ""
display: Keycloak
entity_descriptor:
entity_descriptor_url: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}/protocol/saml/descriptor
issuer: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}
service_provider_issuer: https://mytenant.teleport.sh/v1/webapi/saml/acs/keycloak
assertion_key_pair:
cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
private_key: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
signing_key_pair:
cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
private_key: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
sso: https://<root>/realms/{realm-name}/protocol/saml
version: v2
Update the connector by saving and closing the file in your editor.
Activate client signature validation
-
Navigate to Clients in left sidebar
-
Select your Teleport SAML client
-
Navigate to the Keys tab, and enable "Client Signature Required"
-
Import the converted cert.pkcs12 certificate
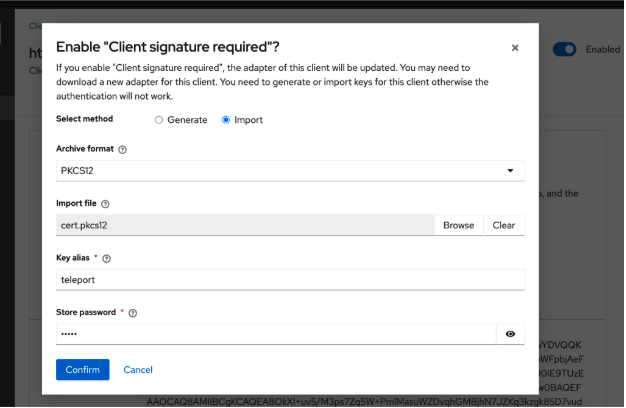
Be sure to enter the correct name and password defined when converting the certificate as the Key Alias and Store Password.
-
Click Confirm to activate it.
If the SSO login with this connector is successful, the client signature validation works.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting SSO configuration can be challenging. Usually a Teleport administrator must be able to:
- Be able to see what SAML/OIDC claims and values are getting exported and passed by the SSO provider to Teleport.
- Be able to see how Teleport maps the received claims to role mappings as defined in the connector.
- For self-hosted Teleport Enterprise clusters, ensure that HTTP/TLS certificates are configured properly for both the Teleport Proxy Service and the SSO provider.
If something is not working, we recommend to:
- Double-check the host names, tokens and TCP ports in a connector definition.
Using the Web UI
If you get "access denied" or other login errors, the number one place to check is the Audit Log. To view the recording, select Audit in the Teleport Web UI, then click Session Recordings in the menu.
Example of a user being denied because the role clusteradmin wasn't set up:
{
"code": "T1001W",
"error": "role clusteradmin is not found",
"event": "user.login",
"message": "Failed to calculate user attributes.\n\trole clusteradmin is not found",
"method": "oidc",
"success": false,
"time": "2024-11-07T15:41:25.584Z",
"uid": "71e46f17-d611-48bb-bf5e-effd90016c13"
}
Teleport does not show the expected Nodes
When Teleport's Auth Service receives a request to list Teleport Nodes (e.g., to
display Nodes in the Web UI or via tsh ls), it only returns the Nodes that the
current user is authorized to view.
For each Node in the user's Teleport cluster, the Auth Service applies the following checks in order and, if one check fails, hides the Node from the user:
- None of the user's roles contain a
denyrule that matches the Node's labels. - At least one of the user's roles contains an
allowrule that matches the Node's labels.
If you are not seeing Nodes when expected, make sure that your user's roles
include the appropriate allow and deny rules as documented in the
Access Controls Reference.
When configuring SSO, ensure that the identity provider is populating each user's
traits correctly. For a user to see a Node in Teleport, the result of populating a
template variable in a role's allow.logins must match at least one of a user's
traits.logins.
In this example a user will have usernames ubuntu, debian and usernames from the SSO trait logins for Nodes that have a env: dev label. If the SSO trait username is bob then the usernames would include ubuntu, debian, and bob.
kind: role
metadata:
name: example-role
spec:
allow:
logins: ['{{external.logins}}', ubuntu, debian]
node_labels:
'env': 'dev'
version: v5
Single sign-on fails with OIDC
When encountering the error message "Failed to verify JWT: oidc: unable to verify JWT signature: no matching keys", it typically indicates a discrepancy between the algorithm used to sign the JWT token and the algorithm(s) supported by the JSON Web Key Set (JWKS). Specifically, the token might be signed with one algorithm, e.g., HS256, while the JWKS only lists keys for a different algorithm. e.g., RS256. This issue predominantly arises when using identity providers that offer extremely low-level functionality.
Here are some things to check:
- Verify the JWT header specifies the correct signing algorithm. This should match one of the algorithms listed in the keys section of the JWKS endpoint response.
- Ensure the JWKS endpoint is returning all relevant public keys. Sometimes key rotation can cause valid keys to be omitted.
To resolve the issue, align the JWT algorithm header with a supported algorithm in the JWKS. Rotate keys if necessary. Verify the JWKS only publishes the active public keys. With proper configuration, the signature should validate successfully.
Signature validation incompatibility
When "Client signature required" is enabled with the appropriate signing keys, it results in an invalid requester error as shown in the image below.
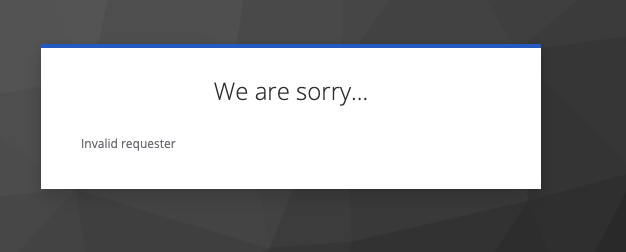
The Keycloak server logs include the error below:
error=invalid_signature and request validation failed: org.keycloak.common.VerificationException: SigAlg was null.
This occurs when Keycloak receives a SAML request that does not meet its signature validation expectations which causes Keycloak to fail when attempting to verify the SAML signature.
To resolve the issue:
- Refer to the Client Certificate Signature validation section to review the certificate configuration. Ensure the certificate is up-to-date and the private key is properly paired with it.
- Once the above has been verified, temporarily add the
spec.provider: pingparameter to the Keycloak auth connector to match Keycloak strict signature requirements.